Overview
Kubernetes集群的访问权限控制由kube-apiserver负责,由Authentication,Authorization,Admission Control三步骤组成:
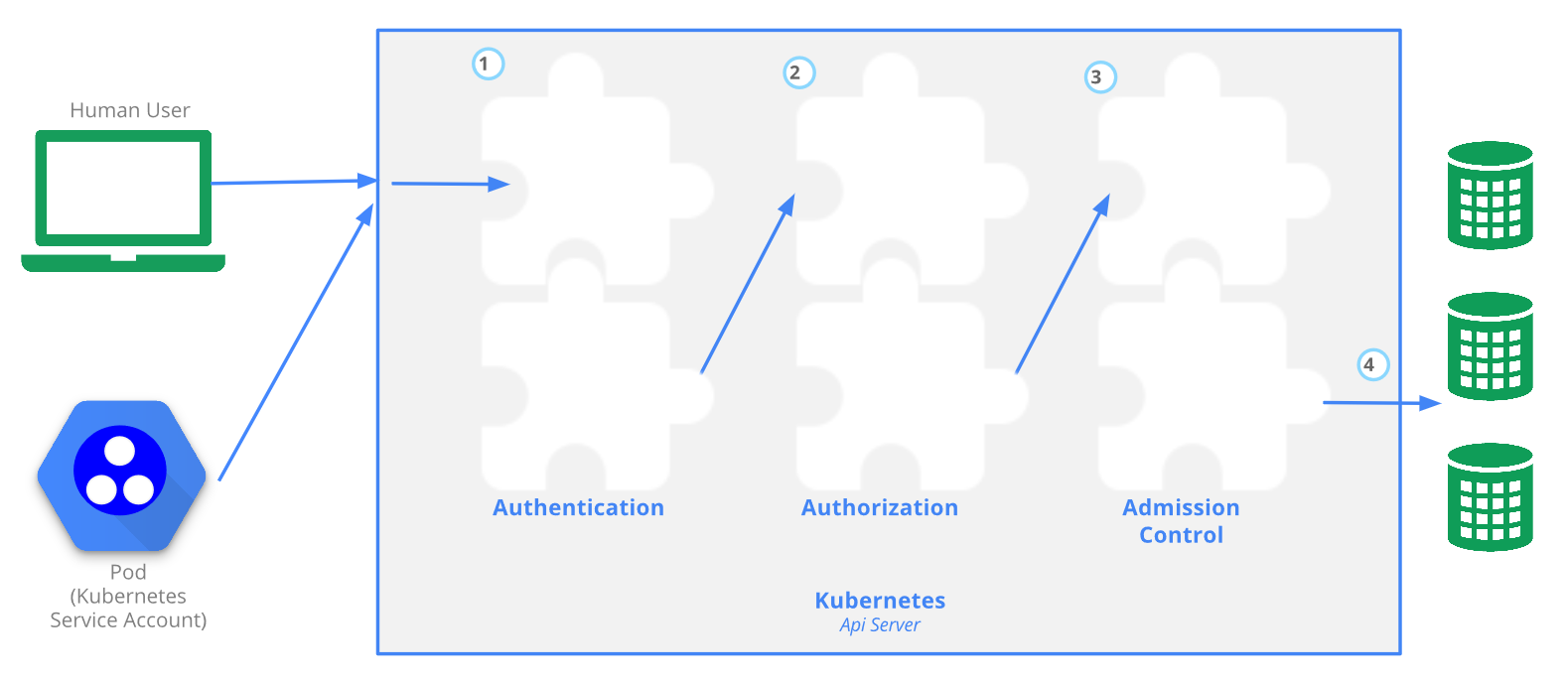
Reference:
认证 Authentication
认证,身份验证,这个环节面对的输入的整个http request。 有CA证书认证,token,basic auth等多种认证方式。认证信息里面会包括用户身份信息,如user,group等,在后面授权环节使用。
kubeadm部署的集群,默认配置了CA和service account两种认证方式。
CA 认证
token 认证
密码 认证
授权 Authorization
Kubernetes中所有的API对象都保存在ETCD中,所有对API对象的操作(增删改查)都需要通过kube-apiserver实现。需要APIServer做授权工作。完成授权工作的机制,就是RBAC。
kubeadm部署的集群,默认配置的认证方式node,RBAC
RBAC
Reference:
RBAC: Role-Based Access Control
Role: 角色,一组规则,定义了一组对API对象的操作权限。有两种:Role和ClusterRole。
Subject: 被作用者,可以是“人”,“机器”,也可以是Kubernetes定义的User。
RoleBinding: role和subject的绑定关系。也有两种:RoleBinding和ClusterRoleBinding。
Role
Role对象只能用于授权对某单一namespace中的资源的访问权限,比如Pod。
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: mynamespace
name: example-role
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
ClusterRole作用于None-namespaced对象,比如Node,定义里面少了namespace的定义。
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: example-clusterrole
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
Subject
Reference:
User
这是一个授权系统里面的逻辑概念,Kubernetes里面没有一个叫User的API对象,在部署和使用的流程中也不需要User,也没创建过User。
User需要通过外部认证服务来提供,比如Keystone。或者,也可以直接给APIServer指定一个用户名,密码文件,授权系统可以从文件里找到对应的User。
大部分情况下使用系统内置的User就足够了。
User是给人用的,命名需全局唯一,None-namespaced。
ServiceAccount
需要绑定到指定的namespace,是给Pod里面的进程使用的。并关联一套凭证,存在Secret里面,这些凭证会同时被挂载到Pod里。
有ServiceAccount的API对象,可以手动创建,也可以api-server自动创建。
默认ServiceAccount是default,对应default的secret。有访问APIServer的绝大多数的权限。
$ kubectl get sa default -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2018-12-07T07:02:13Z"
name: default
namespace: default
resourceVersion: "332"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/default/serviceaccounts/default
uid: 060d1f4e-f9ee-11e8-924c-080027c2b927
secrets:
- name: default-token-782hd
RoleBinding
RoleBinding给指定的Subject赋予Role的权限,都是在Namespace范围内有效。
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: example-rolebinding
namespace: mynamespace
subjects:
- kind: User
name: example-user
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: example-role
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
ClusterRoleBinding给指定Subject赋予ClusterRole的权限,没有Namespace的限制,作用于所有Namespace。
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: example-clusterrolebinding
subjects:
- kind: User
name: example-user
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: example-clusterrole
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
ServiceAccount是有namespace的限制的.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: etcd-operator
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: etcd-operator
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: default
namespace: etcd